State-Led Efforts to Shield Citizens from AI Overreach
In recent years, the issue of artificial intelligence (AI) has moved center stage not only in boardrooms and research labs but also in state legislatures across the country. With a variety of proposals emerging, state governments are seeking ways to manage AI’s potential while protecting citizens against its misuse. From deepfake videos to automated decision-making tools, the legislative proposals are addressing a range of concerns in what some view as a race against potentially overwhelming technological challenges.
State lawmakers are stepping into the AI arena amid a market that remains full of problems and tricky parts. As such, governments at the state level are presenting strategies that range from comprehensive regulatory frameworks to more focused issue-specific agreements designed to figure a path through diverse and sometimes nerve-racking challenges. The struggle to safeguard individual rights while nurturing innovation has emerged as a central theme in these debates.
Understanding the Bipartisan Divide in AI Legislation
Legislation on AI is not only evolving rapidly but is also reflecting the political climate. One striking feature of the 2025 legislative session is the partisan split in proposed AI bills. An analysis of the proposals shows that roughly two-thirds of the bills were introduced by Democrats, while Republican lawmakers have put forward one-third of the measures. Though there have been small bipartisan efforts, much of the push comes from parties following their traditional perspectives on regulation and innovation.
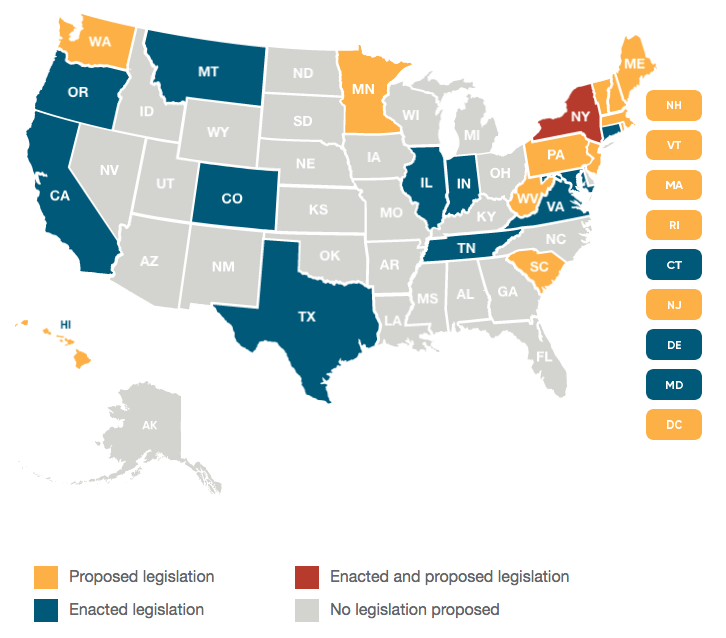
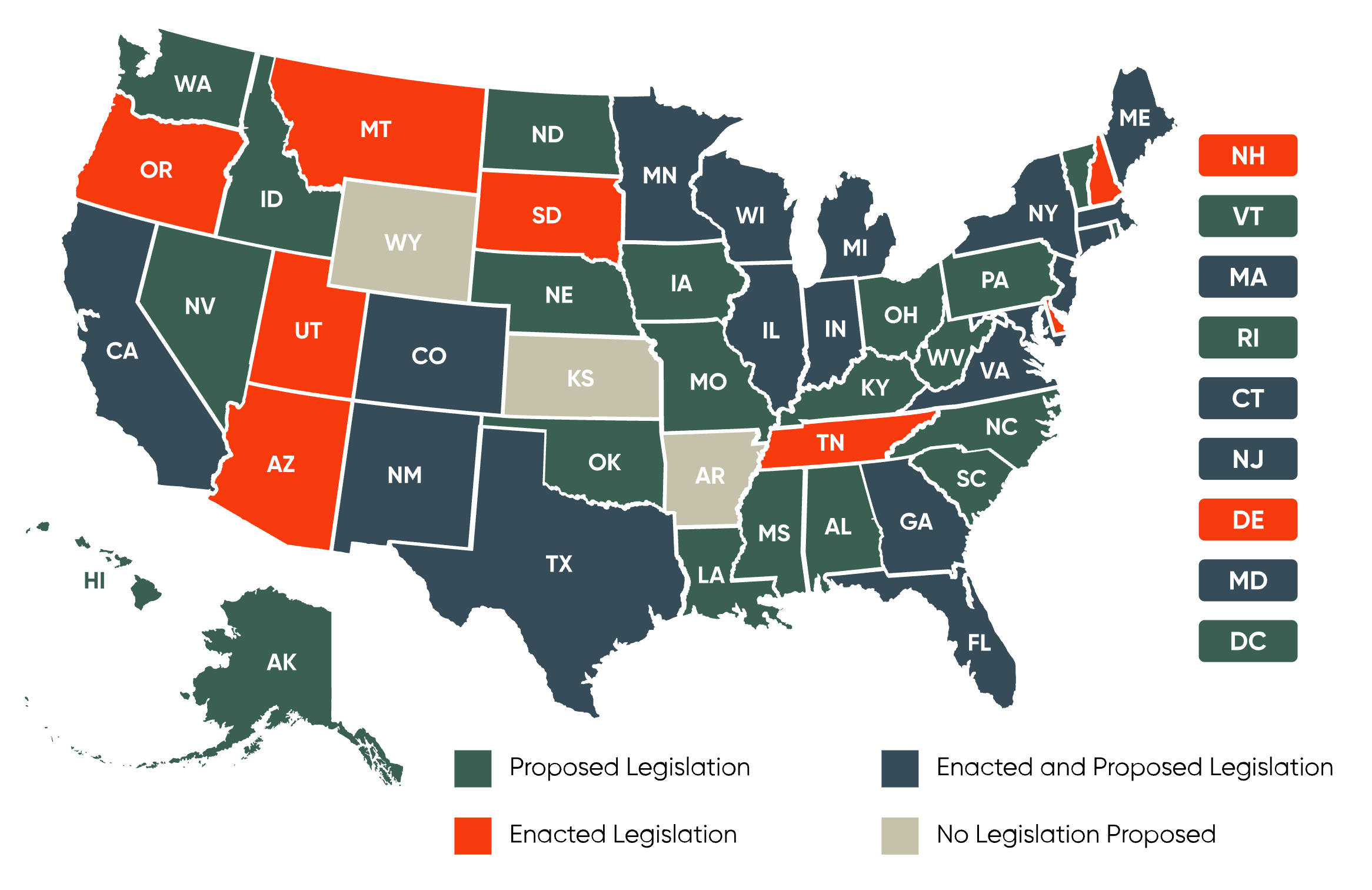
Democrats tend to favor more comprehensive regulatory approaches that impose strict obligations on developers and businesses. In states such as California, New York, and New Jersey, the focus is often on protecting citizens from potential harms by establishing detailed frameworks. On the other hand, Republican-led states generally promote lighter-touch policies aimed at fostering innovation while banning particular harmful practices. This distinction highlights different strategies in addressing not only the benefits of AI but also the pitfalls that come with its deployment.
AI Legislation Targeting Deepfakes and Nonconsensual Imagery
A significant concern cutting across state legislatures is the misuse of AI to generate deepfakes and create nonconsensual intimate imagery (NCII). These bills are driven by a need to protect individuals from the manipulative use of synthetic media, which can lead to personal, social, and even political harm.
For instance, several states have proposed bills that require online platforms to implement processes for victims to quickly request the removal of nonconsensual imagery. Other proposals include hefty penalties for those who knowingly disseminate deepfakes or synthetic NCII content. Although many of these proposals have yet to become law, the emphasis on disclosure and prohibition in legislative language underscores a common goal: to shield citizens from the tangled issues created by rapidly advancing digital tools.
- Mandatory take-down processes on digital platforms
- Prohibitions on the malicious use of synthetic media
- Significant penalties to deter violators
While most of these initiatives remain in committee or have died on the legislative floor, their very introduction is a clear signal that states are aware of and responding to such problematic practices.
Election Integrity in the Age of AI-Driven Disinformation
Another prime area of legislative focus is the use of AI in the political arena, especially regarding elections. Bills introduced in several states aim to address concerns about the potential misuse of AI to influence electoral outcomes. Legislators are probing into proposals that require candidates and political entities to disclose any use of synthetic content in campaign materials.
Some states have taken a more assertive approach by proposing laws that would ban candidates or opponents from intentionally distributing deepfake videos or altered images designed to deceive voters. These measures are intended to ensure a level playing field and to maintain public trust in the democratic process.
The challenge remains, however, given that much of the proposed legislation around elections is still in committee. Often, debates center on identifying the fine points between protecting free speech and preventing deceptive practices, making this an area full of problems and subtle parts that require careful consideration by legislators and stakeholders alike.
Enhancing Transparency in Generative AI Systems
The push for greater transparency in generative AI systems reflects society’s growing unease about interactions with increasingly sophisticated chatbots and digital assistants. Lawmakers are considering measures that would require companies and government agencies to clearly disclose when AI tools are in use. This proposed framework aims to ensure that consumers are not misled into believing they are interacting with human agents.
For instance, bills from states like Hawaii and Massachusetts include provisions for conspicuous notifications when a chatbot is engaged in commercial or public communication. Some proposals even require developers to set up “red teams” to test whether watermarks or other indicators of AI usage can be removed or circumvented.
- Clear labeling of AI interactions
- Red teaming for testing transparency measures
- State reporting requirements to ensure compliance
These efforts attempt to dig into the subtle parts of technology-driven consumer protection. Despite some legislative measures dying on the floor and others lingering in committee, these debates signal an essential rethinking of how AI transparency can be embedded in commercial practices.
Managing High-Risk AI and Automated Decision-Making Tools
Legislation addressing high-risk AI technology—often manifested through automated decision-making tools (ADMT)—is gaining traction among state lawmakers striving to reduce unintended harmful consequences. Many of these bills take inspiration from Colorado’s AI Act, which focuses on algorithmic discrimination and transparency in decisions that significantly impact individuals’ lives.
Key elements include requirements for AI system developers and deployers to:
- Implement checks to ensure AI decisions are non-discriminatory
- Clearly disclose when AI is used as a substantial factor in decision-making
- Establish clear monitoring and accountability frameworks
The bipartisan interest in regulating high-risk AI is partly driven by the fear that such systems, if left unchecked, could lead to decisions that have far-reaching impacts, from employment to housing and beyond. Several states, including Georgia, Illinois, Iowa, and Maryland, have tried to stamp out these risks with well-intended but often challenging proposals. While legislative progress remains uneven—some bills have died in committee while others continue to be shaped—the drive to protect citizens from the confusing bits of automated AI decision-making reflects a growing recognition that technological innovation must be balanced by appropriate oversight.
Government Use of AI: Balancing Innovation with Accountability
The debate over government use of AI brings unique complications as public institutions try to integrate new technologies while upholding transparency and accountability. Recent legislative proposals target the use of AI by state and local agencies to mitigate risks and ensure that any decision driven by AI can be reviewed by a human. The underlying message is one of caution, urging governmental bodies to be mindful of the potential for AI misuse in public administration.
For example, one proposed “AI Accountability Act” would establish a dedicated state board designed to oversee government use of AI, detailing clear goals and data privacy requirements. In contrast, legislation in Montana—recently signed into law—places limits on how extensively state and local governments can use AI, mandating human oversight in critical decision-making processes.
In essence, these measures are not about hindering technological progress but about finding a balanced way to get around potential abuses. Legislators are essentially trying to figure a path through the twists and turns that AI introduces into conventional governance frameworks, ensuring that technological innovations do not eclipse fundamental principles of accountability.
Employment Protections: Safeguarding Workers in the AI Era
One of the most personal impacts of AI has been its influence on the workplace. Concerns about automated decision-making in recruitment and employee management have spurred state lawmakers to introduce legislation designed to protect workers. These measures largely focus on ensuring transparency and fairness in hiring practices and the use of AI-driven employee surveillance.
Legislative proposals include requirements that employers notify job applicants if AI is used in the hiring process. Similar rules extend to workplace surveillance, with certain states seeking to restrict how employers employ AI to monitor worker performance. These initiatives aim to address the fine details of how technology might inadvertently introduce bias or cause unintended consequences in employee evaluations.
- Mandatory notifications when AI is used in recruitment
- Restrictions on AI-based employee surveillance practices
- Measures to ensure fairness in automated decision-making systems
Worker-focused legislative proposals reflect broader societal concerns about the economy in the age of automation and serve as a reminder that technology should support, rather than undermine, workers’ rights and privacy.
Health Care Legislation: Addressing AI in Medicine
Perhaps one of the most critical areas under review is the impact of AI in health care. With AI tools increasingly used for diagnostic, therapeutic, and administrative functions, lawmakers are paying careful attention to ensure that these models do not compromise patient safety and ethical standards.
In California, for example, legislation has been introduced to prohibit terms that imply that AI-based systems confer medical licensure or certification. Meanwhile, Illinois has advanced proposals that would ban health care professionals from relying solely on AI for therapeutic decisions and treatment recommendations without human oversight. Even as AI becomes a super important tool for improving outcomes, these bills underscore the need to implement checks to ensure that technological innovation does not outpace the safety and rights of patients.
- Prohibiting misleading claims about AI medical qualifications
- Mandating disclosure when AI tools contribute to diagnosis and treatment
- Requiring qualified human oversight in AI-driven therapy recommendations
This measured approach helps balance the promise of AI in health care with the reality that any over-reliance on technology can lead to unintended and sometimes overwhelming outcomes.
Federal Challenges and Their Potential Impact on State Legislation
While states are forging diverse paths in AI governance, it is important to consider the federal context. Recent actions in Congress have included proposals—albeit briefly entertained—to institute a moratorium on state AI regulation. Although the idea of a 10-year moratorium was ultimately dropped, it remains a reminder that federal policies could soon shape or even constrain the progress made at the state level.
Many state lawmakers fear that federal overreach could negate the progress they have made. The tension between state initiatives and federal oversight is an ever-present issue—that federal guidelines may soon demand a unified national strategy for AI regulation, potentially stifling the nuanced approaches developed within each state.
Nonetheless, until federal authorities impose uniform regulations that preempt state law, it appears that states are likely to continue pressing hard on tailored AI legislation. The current landscape is a patchwork of proposals—each shaped by local experiences and concerns—that together paint a picture of a nation keen on protecting its citizens from the overwhelming and at times confusing bits of AI technology.
Lessons Learned from a Decade of AI Oversight Initiatives
Looking back over the past decade, there are several lessons that emerge for policymakers at both the state and federal levels. First, the need to protect individual privacy and maintain transparency is a recurring theme in virtually every AI-related bill. Whether dealing with nonconsensual imagery, election interference, or high-risk AI systems, the insistence on disclosure and regulation appears as a unifying principle across diverse legislative proposals.
Second, the importance of balancing innovation and regulation cannot be overstated. States that have taken a piecemeal approach—addressing specific issues rather than enforcing a comprehensive framework—reflect the challenge of balancing the positive potential of AI with its possible risks. This approach allows for flexibility, letting legislators steer through the little details and subtle parts of each issue as technology evolves.
- Emphasis on protecting citizens through clear disclosure requirements
- Adoption of measures that strike a balance between nurturing innovation and ensuring safety
- Varied approaches that reflect regional priorities and experiences
The diverse state responses offer a de facto playbook for how governments might manage the complex public policy issues that AI presents. By carefully considering each measure’s strengths and weaknesses, states can better craft legislation that guards against potential harms without discouraging technological progress.
Looking Ahead: The Future of AI Legislation
As the debate on AI regulation moves forward, several key challenges lie ahead. With proposals varying significantly in scope and detail, stakeholders have been left to wonder which models will serve as the best safeguards for citizens. It is clear that state governments have taken a lead in this space, developing innovative proposals aimed at addressing the nitty-gritty of AI’s impact on daily life. Yet, the specter of federal intervention remains.
For the time being, states are likely to continue pressing ahead with legislation that reflects both local sensitivities and national concerns. The interplay between federal guidelines and state innovation will require careful monitoring, as a misstep at either level could inadvertently allow AI systems to become even more intimidating in their reach.
Recent trends suggest that areas where tangible harm is directly observed—such as control over nonconsensual imagery or election manipulation—will remain at the top of the legislative agenda. As each state experiments with different regulatory models, there is hope that best practices will emerge and eventually inform a more unified national strategy.
Overall, while some proposals are still only on paper and others have been stalled by committee challenges, the conversation has already shifted. The process of crafting these policies is a vivid demonstration of how governments are trying to steer through a landscape filled with the confusing bits of emerging technology. By working through the tangled issues and slight differences in approach, both state and federal policymakers hope to achieve a balanced and effective AI governance framework in the years to come.
Key Takeaways for Policymakers and Industry Stakeholders
For policymakers and industry stakeholders alike, the current legislative landscape offers several practical lessons:
- Clear Communication and Transparency: Make it clear when and how AI is used, ensuring both consumers and citizens understand their rights and the technology’s role in decision-making.
- Balanced Regulation: Strive for a regulatory framework that protects citizens from harmful AI applications while still encouraging innovation and economic growth.
- Localized Approaches: Recognize that different states may prioritize various aspects of AI governance, from employment protections to election security, allowing for experimentation and refinement.
- Coordination with Federal Authorities: Prepare for potential federal oversight that may harmonize disparate state efforts, ensuring that state-level ingenuity is not lost amid broader regulatory changes.
These takeaways underline a future where technological innovation is a double-edged sword—one that offers tremendous benefits if managed with care, but which also requires vigilant oversight to prevent abuse.
Charting a Path Forward with Collaborative Efforts
The current debate around AI legislation is a reminder of the power of collaborative policymaking. By drawing on lessons from both domestic and international experiences, states are crafting solutions that complement broader trends in global AI governance. Notably, initiatives like the Partnership for Global Inclusivity on AI and joint infrastructure investments with other nations further illustrate the value of collaborative approaches in addressing the overwhelming technology-driven challenges of our time.
Cooperative efforts can help mitigate the complexities of a fragmented regulatory environment. As states experiment with different models—from comprehensive legislation to more focused, issue-specific bills—there remains a promising opportunity to plug these varied approaches into a cohesive national strategy.
| Focus Area | Key Legislative Actions | Current Status |
|---|---|---|
| Nonconsensual Intimate Imagery (NCII) | Take-down procedures; heavy penalties; prohibition measures | Multiple bills introduced, most stalled in committees |
| Elections | Disclosure requirements for AI-driven content; ban on deepfakes | Several proposals pending, with bipartisan interest |
| Generative AI Transparency | Clear notifications on AI use; red team testing requirements | Some bills stalled while others remain in committee |
| Automated Decision-Making & High-Risk AI | Protection against algorithmic discrimination; transparency obligations | Inspired by Colorado’s model, with mixed legislative results |
| Government Use of AI | Oversight boards; disclosure of AI use in public administration | Varies by state; some proposals recently signed into law |
| Employment | Notification in hiring; restrictions on surveillance | Ongoing debates in several state legislatures |
| Health Care | Disclosure in medical AI use; limitations on AI-based care decisions | Some bills signed into law, others pending review |
This table helps to highlight the diverse approaches taken across states, showcasing how different regions are addressing both the opportunities and the challenges presented by AI. It is through a blend of localized creativity and national-level coordination that effective AI oversight can be achieved.
Conclusion: Embracing a Future of Balanced AI Governance
The landscape of AI legislation is evolving amidst a backdrop of fast-moving technological change and political debate. State lawmakers are at the forefront of this development, crafting rules designed to protect citizens from the unintended and sometimes overwhelming consequences of new AI applications. While debates continue over the precise balance between protecting individuals and fostering technological progress, what is clear is that the time has come for robust, state-led action.
The diverse proposals—from measures targeting nonconsensual imagery to those addressing high-risk automated decision-making—reflect a determined effort to manage the little twists that come with AI innovation. Even as federal efforts loom large on the horizon, state governments are taking a proactive stance, often under challenging conditions and in partnerships with international allies, to create a legislative playbook that may well serve as a model for future national regulation.
In the coming years, we can expect that these initiatives will experience further refinement as states continue to work through the tangled issues and subtle parts of AI regulation. For policymakers, industry leaders, and citizens alike, the journey toward balanced AI governance is one that requires sustained attention, creative problem-solving, and a willingness to negotiate between innovation and public safety.
Ultimately, while the technology itself may be both inspiring and intimidating, careful and collaborative legislation may prove to be our best means of harnessing its benefits while ensuring that its risks are kept in check. As states continue to spearhead this vital regulatory effort, their individual experiments with transparency, accountability, and protection will no doubt inform a broader strategy for managing AI in America—and possibly around the globe.
Originally Post From https://www.brookings.edu/articles/how-different-states-are-approaching-ai/
Read more about this topic at
States Can Continue Regulating AI—For Now | Brownstein
US state-by-state AI legislation snapshot